ASTM A500/A500M–13
Most users of HSS are now aware of the new ASTM A1085 specification for “higher performance” HSS that was approved in 2013 and immediately manufactured by Atlas Tube. Details of the features of this HSS are readily available: http://www.atlasconnection.com/profiles/blogs/new-astm-specification-provides-improved-performance-for-hollow
In 2013, however, an updated edition of the familiar ASTM A500 specification was also released (ASTM A500/A500M–13). This had two slight modifications:
(i) Clause 5.1: The permitted processes to produce the steel were reduced to basic-oxygen and electric-furnace. Thus, the open-hearth process was removed, reflecting current practice.
(ii) Clause 6.3: A new requirement for the HSS weld seam was added … “The weld shall not be located within the radius of the corners of any shaped tube unless specified by the purchaser”.
It is generally accepted by HSS manufacturers that longitudinal seam welds should not lie in the corner regions of square and rectangular HSS. There is a lack of experience and testing to support the approval of corner seam welds in regions of high cold-forming, for any structural application, so this “best practice” condition was added to A500. In ASTM A1085-13, however, this prohibition of the seam weld in the corner is not included – yet. Thus, a weld seam located beyond the tangent point of an HSS “flat” is cause for rejection of ASTM A500 material, but not ASTM A1085 material at present.
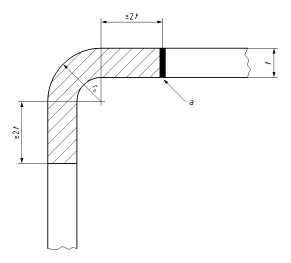
It is worth noting that a recent international standard for HSS welded connections, ISO 14346 (ISO, 2013), also contains an informative (i.e. not “normative” or mandatory) “Annex A: Quality requirements for hollow sections” which advises against longitudinal seam welds in the corner regions of square and rectangular HSS made by cold-forming. This standard even states that the distance between the longitudinal seam and the tangent point to the flat should be at least two times the HSS wall thickness, as shown in Fig. 1, and sometimes greater. This confirms that there are precautions necessary when welding in regions of high cold-forming.
References
ASTM, 2013. “Standard Specification for Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and Shapes”, ASTM A500/A500M–13, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA.
ISO, 2013. “Static Design Procedure for Welded Hollow-Section Joints – Recommendations”, ISO 14346:2013(E), International Standards Organisation, Geneva, Switzerland.
Fig. 1: Seam weld position requirement in ISO 14346:2013(E)